Otoplasty
If protruding or disfigured ears bother you or your child, you may consider plastic surgery. Ear surgery — also known as otoplasty — can improve the shape, position or proportion of the ear. It can correct a defect in the ear structure that is present at birth, that becomes apparent with development or it can treat misshapen ears caused by injury.
Consultation with Dr Philip Fleming is the best way to determine how ear surgery can help you achieve your personal goals. Dr Fleming is certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery, Inc and he has more than 25 years of experience in performing ear surgery. The following is an overview of ear surgery procedures.
Procedural Steps
Step 1 – Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedure. The choices include local, intravenous sedation or general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
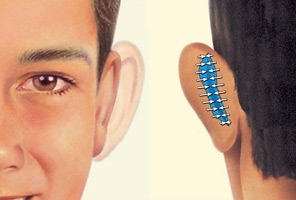
Step 2 – The incision
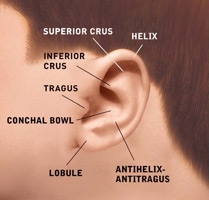
Correction of protruding ears uses surgical techniques to create or increase the antihelical fold (just inside the rim of the ear) and to reduce enlarged conchal cartilage (the largest and deepest concavity of the external ear). Incisions for otoplasty are generally made on the back surface of the ear. When incisions are necessary on the front of the ear, they are made within its folds to hide them. Internal, non-removable sutures are used to create and secure the newly shaped cartilage in place.
Step 3 – Closing the incisions
External stitches close the incision. Techniques are individualized, taking care not to distort other structures and to avoid an unnatural “pinned back” appearance.
Step 4 – See the results
Ear surgery offers near immediate results in cases of protruding ears, visible once the dressings that support the new shape of the ear during initial phases of healing are removed. With the ear permanently positioned closer to the head, surgical scars are either hidden behind the ear or well-hidden in the natural creases of the ear.